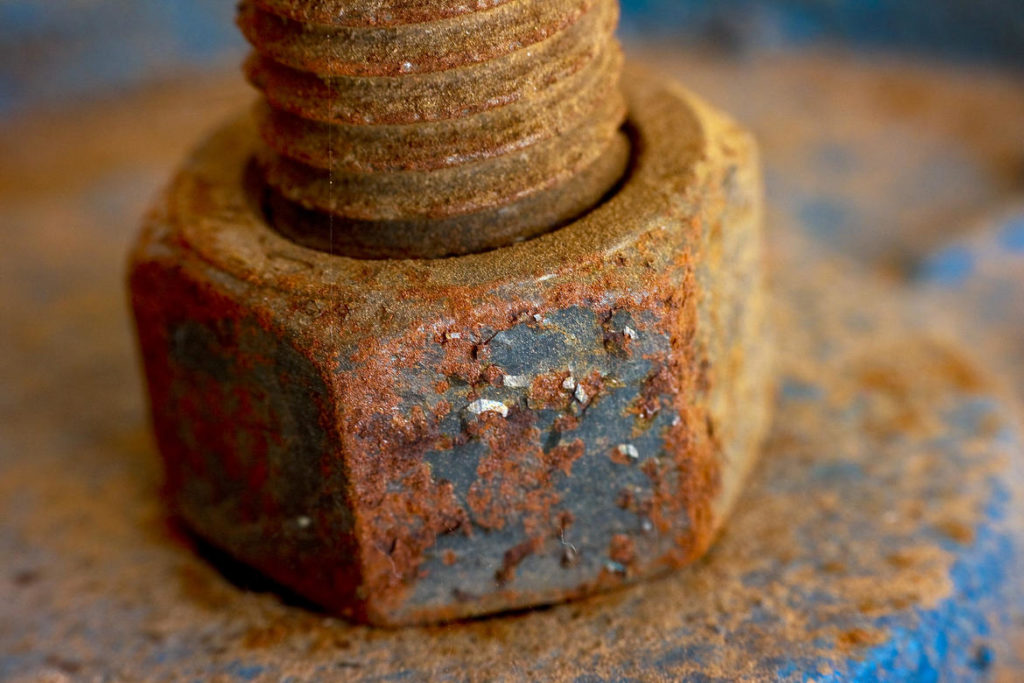
Rust is a common phenomenon for iron and steel appliances and equipment. Rust causes metal surfaces and objects to become soft, easy to peel, and easily crumbles into powder. Therefore, it is very important to find out the cause and find a solution to fix it. In this article, Qualitas DC will help you better understand these issues.
What is rust?
Rust is the phenomenon of iron surface forming a reddish brown paint due to the action of moist air. Rust is the result of metal oxidation, which is the combination of iron metal with oxygen in the air.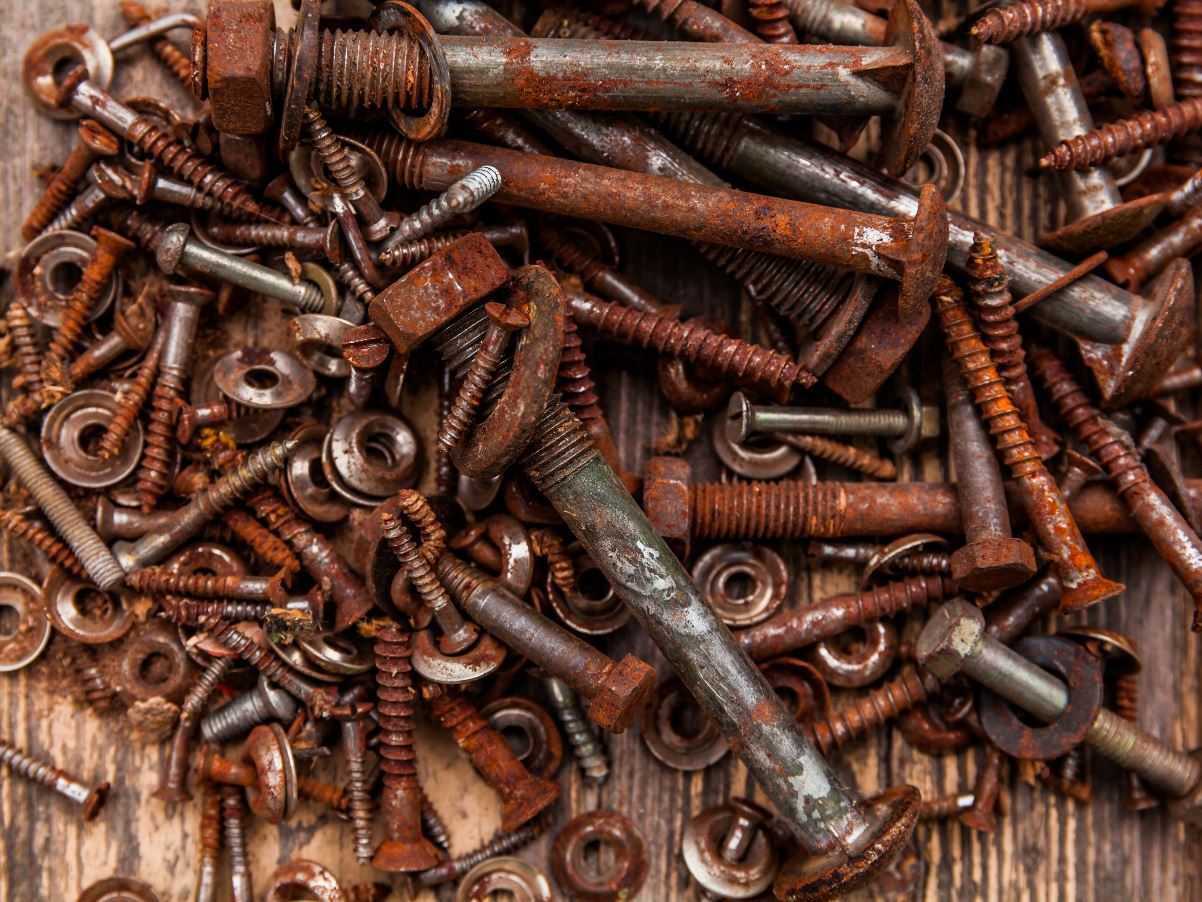
Rust and steel are the most common examples of metal corrosion. This rust layer causes many harms, reducing the hardness of the metal layer. The layers of rust over time gradually peel off, causing the layer of materials to wear out, change color, and change properties.
For example: Rusted iron nails are very easy to break, creating rust holes on the surface of the material. The rusted pieces of iron will be in the form of a sponge-like texture, so it easily absorbs water and quickly rots.
What causes rust?
Rust is a natural process that occurs with ferrous metals. Utensils, equipment, and machines are often made from steel or alloys with high iron content, so they cannot be avoided.
2.1. The main cause of rust
There are many factors that contribute to rust formation, including the humidity in the air and the pH of the surrounding environment. Here are a few of these factors:
Humidity: The presence of water in the surrounding environment causes corrosion of metal surfaces. The most common cause of rust formation is exposure to rainwater.
Specifically: The rusting process is faster if the pH of the surrounding metal is low (acidic environment). When iron is exposed to rain (usually containing) acids, the iron surface will rust faster.
Or due to the presence of different salts in the water, iron rusts faster. Many ions in water accelerate rusting through electrochemical processes.
Impurities: When compared to iron with many metals, pure iron rusts more slowly.
In addition, the size of an iron object can also affect its rust rate. For example, a giant iron object may have small cracks due to the metallurgical process. These vulnerabilities allow elements from the environment to attack the metal.
2.2. Chemical reactions lead to rust
Oxygen is a very good oxidizing agent, and iron is a reducing agent. Therefore, the iron atom easily gives up electrons when exposed to oxygen. Oxidation of iron can take place through the following reactions:
Fe → Fe2+ + 2e–
The oxidation state of iron is further increased by the oxygen atom in the presence of water:
4Fe2+ + O2 → 4Fe3+ + 2O2-
Now, the following acid-base reactions occur between iron cations and water molecules:
Fe2+ + 2H2O ⇌ Fe(OH)2 + 2H+
Fe3+ + 3H2O ⇌ Fe(OH)3 + 3H+
Iron hydroxides are also formed from the direct reaction between iron cations and hydroxide ions.
O2 + H2O + 4e– → 4OH–
Fe2+ + 2OH– → Fe(OH)2
Fe3+ + 3OH– → Fe(OH)3
The formed hydroxides of iron now undergo dehydration to produce the iron oxides that make up rust. This process involves many chemical reactions, some of which are listed below:
- Fe(OH)2 ⇌ FeO + H2O
- 4Fe(OH)2 + O2 + xH2O → 2Fe2O3.(x+4)H2O
- Fe(OH)3 ⇌ FeO(OH) + H2O
- FeO(OH) ⇌ Fe2O3 + H2O
One similarity between all the chemical reactions listed above is that they all depend on the presence of water and oxygen. It can be seen that the environment with a lot of water vapor and high temperature are favorable conditions for oxidation.
What are the effects of rust?
Rust causes many harms to people in life or production activities. Because the structure of iron oxide is not stable, it makes the metal surface weaker, looser and easily broken. Some of the harmful effects of rust can include:
- To a small extent like a rusted nail will no longer be usable. But on a larger scale such as machinery and architectural works, when rusted, it easily leads to collapse and fracture, which takes a lot of repair and maintenance costs.
- Rust can make holes in sheet metal.
- Rust reduces magnetism much more than iron. An iron magnet can still work almost as well when it has a thin layer of rust on it, but if it rusts so badly that most of the metal surface is gone, it won’t work as well as a magnet. Normal.
- Rust is an insulator, meaning it does not conduct electricity easily, unlike iron, which is a conductor of metal. So if some electrical connections are made of iron, it may be damaged when the iron surface is rusty.
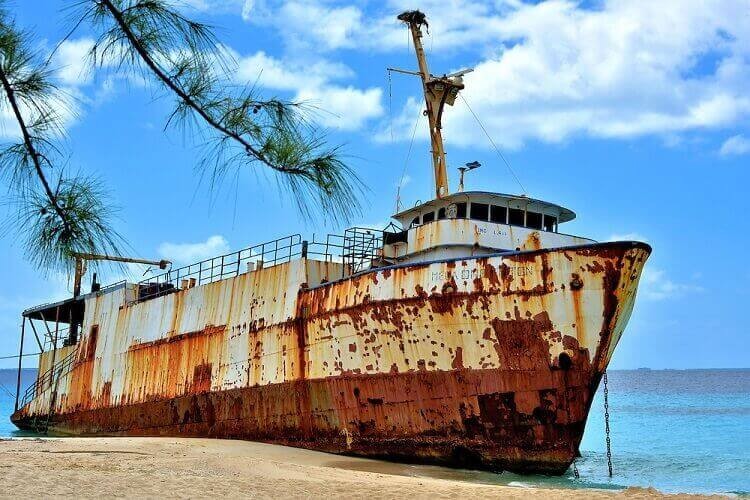

Will other metals rust?
Usually when it comes to rust, we often think of it as a phenomenon of iron metal. Each metal has a different oxidation number and activity level. The shell structure of iron makes it quite chemically active, so under normal conditions iron is easy to rust. Meanwhile, other metals such as silver, copper, zinc, aluminum, nickel, chromium … are more difficult to rust, but not impossible.
>>> See more articles: What is stainless steel? Does stainless steel rust? <<<
Some measures to prevent rust
Our country has a hot and humid climate, with a lot of rain, so iron in the air is easy to rust. Therefore, rust can be controlled by limiting the amount of oxygen and water surrounding the metal. To reduce rust, we can protect iron in two ways from the outside or from the inside. Here are some ways to help slow down and limit the occurrence of rust:
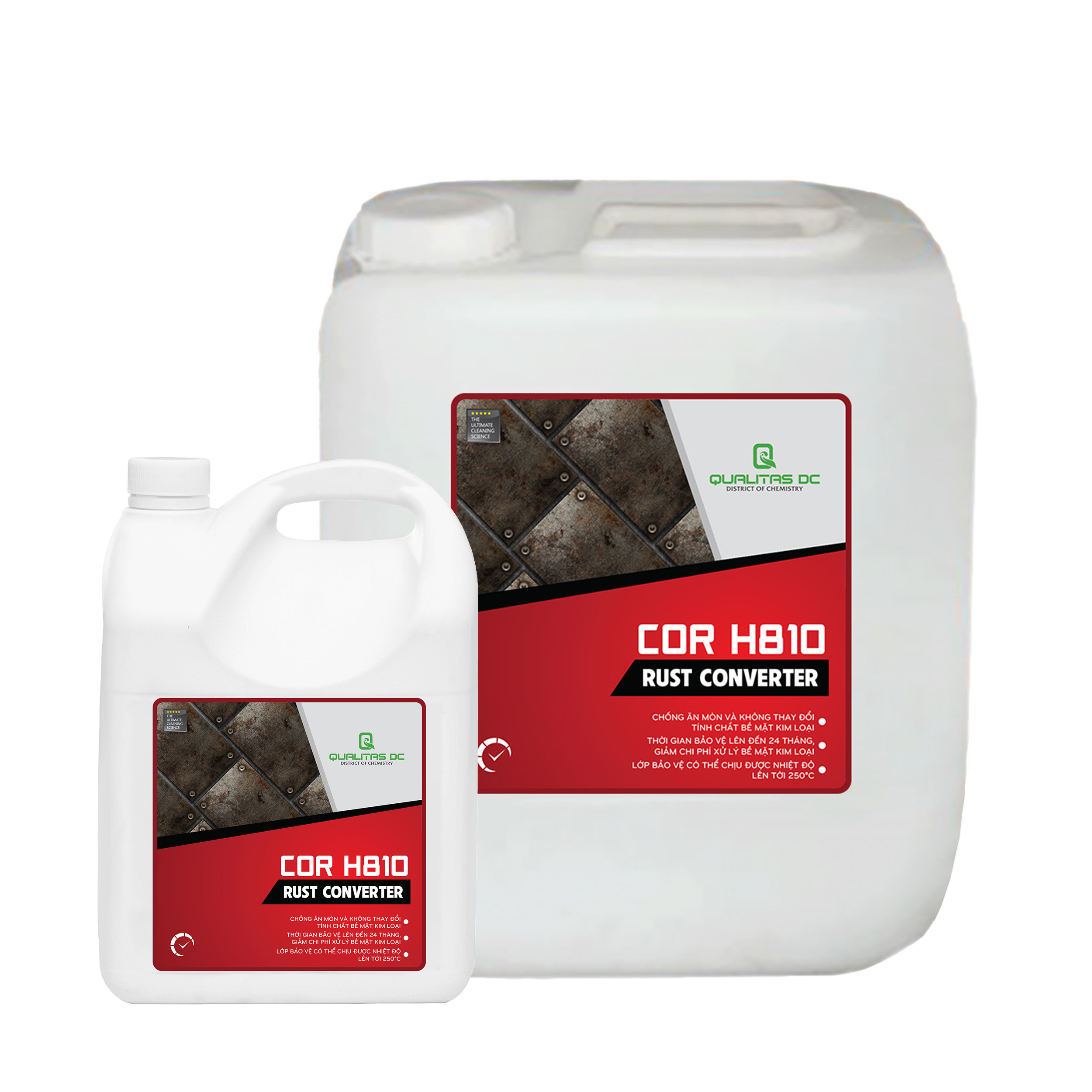
Use rust conversion product COR H810
Rust Remover COR H810 works very well on rusty metal surfaces. With a rusted surface, COR H810 quickly
penetrates the rust, chemically fixing the rust layer and converting it into an inert and water-insoluble organic complex in just a few minutes. Reduce the cost of surface treatment before painting. Metal surface coating with a durable dark purple finish provides long-lasting protection for up to 24 months. Use sparingly because 1 liter of the product can handle 15m2 of surface. Withstands temperatures up to 250°C.
>>> View more products COR H810 <<<
Using coatings on metal surfaces
Various coatings can be applied to exposed metal surfaces to prevent corrosion. Common examples of anti-corrosion coatings include paints, wax tapes, and varnishes.
The outer coatings act as a protective layer to prevent iron and steel from being exposed to the outside air to limit oxidation. In this paint is mixed with rust inhibitors. This method is widely used in large iron and steel works such as ships, wharfs, etc.
Smaller items can be coated with an absorbent oil to prevent the device from rusting. Many industrial machines and tools made of iron are coated with a metal lubricating grease to reduce friction and at the same time prevent rust. However, this method is not completely effective.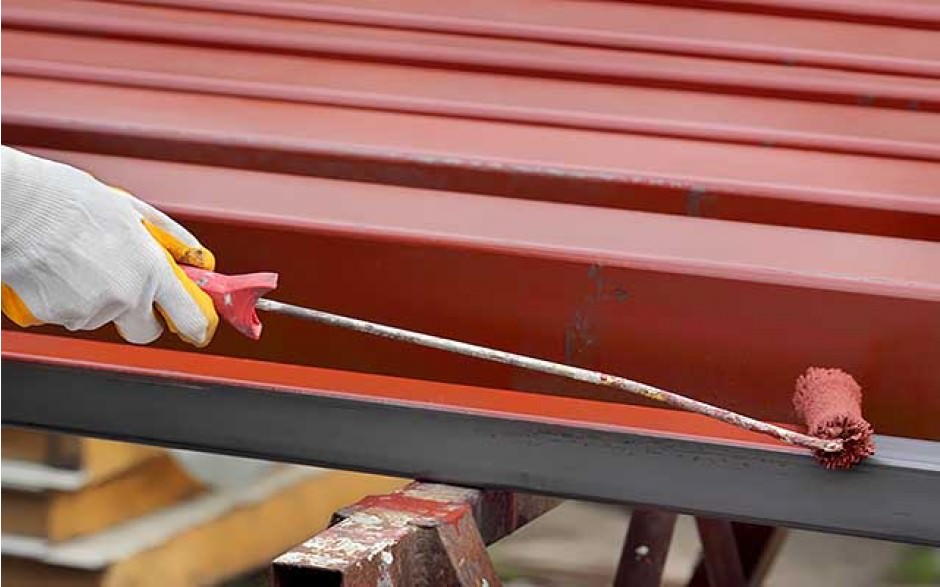
Paint to prevent rust
Galvanizing method
In addition to using paint coating, another layer of metal can be used to cover the outside to protect the steel. The most common method is galvanizing. Zinc is often used because it is cheap and easily adheres to steel.
The disadvantage of galvanizing is that it only protects against corrosion for a limited period of time since the outer zinc layer will corrode first. So it is still not very effective in highly corrosive areas.
Using anti-rust alloy material
In the manufacture of materials, substances will often be added to iron to create anti-rust alloys, such as iron mixed with chromium oxide, nickel because the rusting rate of this alloy is slower than pure iron. At the same time, it is still necessary to combine with protective measures such as using anti-rust coating to avoid exposing the alloy to the outside because the material continues to rust.
Anti-rust alloy fabrication
Humidity control
Because in an environment with a lot of steam and temperature, the oxidation of iron will cause rust to take place faster. Controlling humidity can help slow rust formation. Therefore, equipment and machinery should be placed in a cool place, away from high humidity, away from heat sources and direct sunlight. When transporting machinery and equipment by sea in containers, silicagel packages are often added to absorb moisture.
Through the above article, Qualitas DC has helped readers understand what rust is? Causes, effects as well as measures to help prevent rust. Because this is an inevitable natural phenomenon, applying measures to help slow down and limit the rusting process is a necessary and optimal solution today for appliances, tools, machines and equipment. iron, metal.