We all know, metal is extremely durable and widely used. With many outstanding features such as: electrical conductivity, shape, reuse, … metal is applied in most of the objects around us. So do you know what are the 10 hardest metals ever discovered by man? Let’s also Qualitas DC find out in the article below.
Tungsten
Tungsten is the hardest metal ever known. It is a chemical element with a high density (19.25 g/cm3). In its rare form, tungsten is difficult to machine due to its brittleness, which can change as it turns pure. Very high resistance to abrasion and melting temperatures (3422 °C/6192 °F). This makes it ideal for producing durable metals under extreme conditions. Tungsten also has excellent electrical and thermal conductivity, making it popular in many electronic applications.
Tungsten was discovered in 1781 but was not given a name until much later – derived from the Swedish words for Tung (heavy) and sten (stone). The most obvious applications of tungsten are in light bulb filaments, high-speed cutting tools, etc. In addition, they can be used as alloys in steel materials to increase hardness.
Chromium
Chromium is an essential chemical element for the environment, human health and modern technology. Chromium is a metal belonging to the group of heavy metals, very hard, blue. Chromium is a compound that can be found naturally in soil, plants, and rocks. It makes up about 0.03% of the mass of the earth’s crust. The most common compound of chromium currently found by humans is the chromite ore FeO.Cr2O3.
Chromium is used in industrial processes such as stainless steel production and chromium plating. Chromium’s ability to resist corrosion and retain its luster makes it extremely valuable in products such as coatings on furniture, automobiles, and kitchen appliances.
Chromium is also needed for carbohydrate metabolism, protein digestion and normal growth in the body; Trace minerals should be supplemented daily through the diet in nuts, meat, chicken, peppers and other nutrient-rich foods.
Titan
Titanium is one of the hardest and lightest metals on Earth. It has a tensile strength of about 63,000 psi (pounds per square inch) and a density of just 4.51 grams per cubic centimeter. It is also non-corrosive to seawater and most acids. Even in its pure form, titanium is harder than many steels. As a refractory metal, it is highly resistant to heat and abrasion.
That is why titanium and its alloys are so popular. For example, it can be used to make alloys with iron and carbon. Titanium is especially ideal for manufacturing applications in medical and other industries. It is also used in aeronautical engineering due to its stiffness and weight ratio. When combined with aluminum, it creates an extremely strong yet lightweight material that can withstand high temperatures.
Gadolinium
Gadolinium is a relatively rare silvery-white metal in the Earth’s crust. Gadolinium is known for its unique magnetic properties. It is a paramagnetic material, which means it is attracted to a magnetic field and can easily be magnetized. This property makes gadolinium useful in many different applications such as the electronics industry, especially in the field of medicine.
Gadolinium is also used in the production of phosphorus for various applications including television screens and fluorescent lamps. It is a key ingredient in creating bright and vibrant colors in these devices.
In addition, Gadolinium has several nuclear applications. It can be used as a neutron absorber in nuclear reactors to control the rate of nuclear fission. It is also used in the production of some fuels for nuclear power plants.
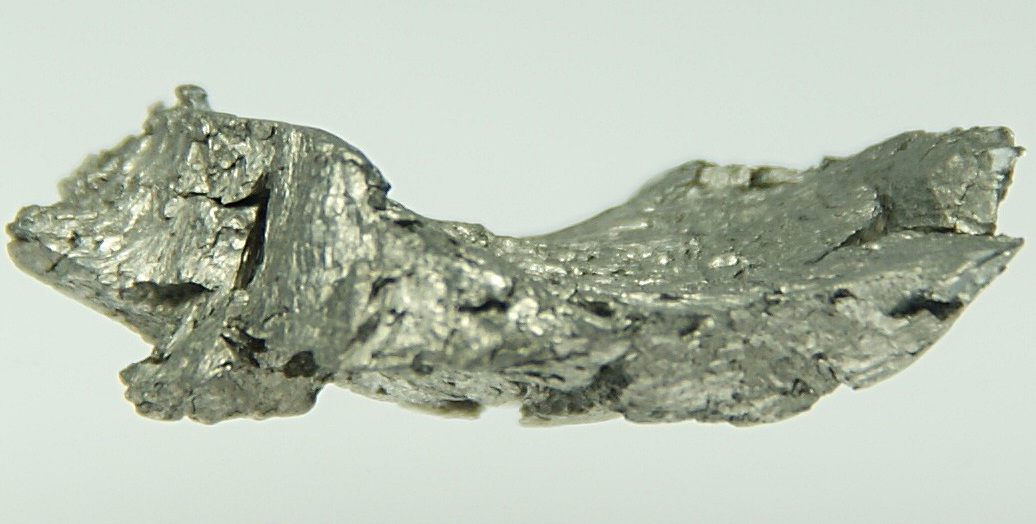

Iron
Iron is one of the most abundant elements on earth, symbol Fe and atomic number 26. Iron is grayish-white in color, but it oxidizes to a reddish-brown color in the air. Due to its hardness, durability and affordable price, iron is often used in the production of steel, which is a widely used material in the construction, manufacturing and transportation industries. Steel is made by combining iron with a small amount of carbon to increase strength and hardness.
In addition to being found in a wide variety of everyday products from furniture and cookware to infrastructure components, iron is also essential for our bodies. Iron helps maintain muscle function and also carries oxygen through the blood which contributes to overall health. Iron is certainly an elemental wonder with its myriad uses.

See also: Does stainless steel rust?
Osmium
Osmium is a very heavy and toxic transition metal element, with the symbol Os and atomic number 76. It is the heaviest metal and the highest density element of all natural elements, with a density of 22.59 g/cm3 (50.29 oz/in3). This element is quite brittle and has a very high melting point (3033 °C). Osmium is an extremely rare, silvery-white, bluish-white metal that is volatile and has a very unpleasant odor, making up about 10 parts per million of the mass of the Earth’s crust. This makes Osmium one of the hardest metals to obtain commercially.
Osmium has excellent corrosion resistance, making it suitable for use in electrical contacts where resistance to wear or oxidation is required. This is one of the components that play an important role in making alloys. Especially stainless alloys are used to seal the tip of pen nibs or hinge tools. In addition, this metal is also widely used in the medical industry.
Zirconium
Zirconium is an extremely versatile chemical element of the transition metal group, symbol Zr and with atomic number 40. Zirconium is a grayish-white, lustrous metal with high strength and difficulty in oxidizing.
One of the main uses of Zr is in the production of nuclear reactors. Zirconium alloys, such as zircaloy, are used as coating materials for fuel rods in nuclear power plants. These alloys have excellent corrosion resistance and can withstand high temperatures, making them ideal for storing and protecting nuclear fuel.
Zirconium is also used in the manufacture of ceramics and various refractory materials. Zirconium dioxide, or zirconia, is a highly stable and heat resistant compound used in the manufacture of porcelain crowns, artificial gems, and high performance ceramics for industrial applications. It is even used as an insulation on fire extinguishers.
Furthermore, Zirconium compounds are used as catalysts in chemical reactions. They can facilitate the conversion of certain compounds into desired products, making them valuable in the production of pharmaceuticals, polymers and other chemical processes.
In addition to these applications, zirconium is also used in the aerospace industry, where it is used to produce light alloys for aircraft parts. It is also used in the manufacture of certain types of glass, such as decorative glass and high refractive index glass used in optical lenses.
>>> See more: What is carbon fiber? Application of carbon fiber <<<