Metal is likened to the backbone of industry, it is an indispensable material in the process of industrial production and construction in the country as well as in the world. However, with the tropical monsoon climate, high humidity like in our country, metal products are easy to oxidize, causing corrosion and rust. To deal with this problem, many anti-corrosion methods have been studied, one of which is the use of phosphate coating. Chemical Phosphate with the phosphate method was born as a turning point for the metalworking industry.
What is Phosphating?
Phosphating is a chemical preparation used to treat metal surfaces before electrostatic painting.
Phosphating is a widely used industrial metal surface treatment method for metal surface treatment, considered one of the best methods of preparing metal surfaces before coating or dipping. grease to protect ferrous parts.
The phosphate film converts the metal surface to a new surface layer that is no longer conductive and metallic, and is resistant to corrosion. Thanks to these properties, people create phosphate technology for use in metal surface treatment plants.
Mechanism of Phosphate
Phosphate is the process of forming on the surface of metal a layer of metal phosphate insoluble in water. This process is often used to coat ferrous metals such as iron, steel or galvanized steel.
The film is formed based on the reaction of the metal with the dihydrophosphate solution leading to the precipitation of the slightly soluble phosphate salts on the metal surface.
At present, the phosphating processes are usually carried out by spraying directly onto the metal surface a solution of di-hydrogen phosphate salts of metals such as Zn2+, Mn2+, Fe2+, Ca2+, Na2+ or dipping the metal in solutions. This.
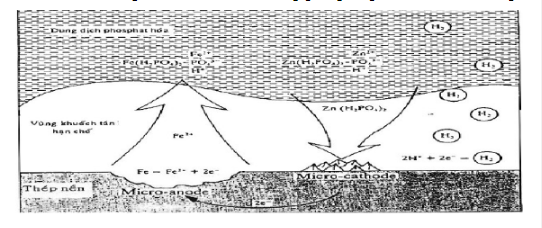
Modeling the process of forming phosphate coating on steel surface
Purpose of phosphate
- Improve metal surface before coating, anti-corrosion primer.
- Create adhesion for plastic and rubber coatings.
- To treat metal surfaces before mechanical processing such as cold rolling, wire drawing, etc.
- To increase the corrosion resistance of grease and wax layers.
Function
Synthesized functions of the Phosphate membrane:
- Link to metal background.
- The base layer of the paint film.
- Increases adhesion of paint film.
- Anti-corrosion under paint.
Its most common effect in practice is to prolong the life of the coating film. The metal base is quite inert to coating materials, the phosphate layer creates a porous film that adheres very firmly to the metal substrate and insulator.
However, the phosphate coating is merely a porous coating, so oils or other sealants are used to achieve corrosion resistance.
Zn2+, Mn2+ coatings are commonly used to help break down corrosive components and prevent roughening.
In addition, the pores allow additional materials (paints) to penetrate the Phosphate coating after drying and to be mechanically interlocked.
Phosphate Process
Phosphate process also known as Zinc Phosphate is a surface processing method widely used in the industrial field to treat metal surfaces before painting. The phosphate film created on the metal surface is no longer conductive and metallic, and is resistant to corrosion.
Phosphate is a sequential technological process following the following steps:
Step 1: Degreasing make sure the phosphate metal surface is free of grease and oil for the best phosphate process.
Step 2: Rinse with water to remove excess degreasing chemicals.
Step 3: Remove rust on metal surface. During the phosphating process, if the details are still rusty, the phosphate layer will be uneven, blistered, and swollen, greatly affecting the quality of the paint. The rust removal process plays an extremely important role.
Step 4: Wash with water remove the acid on the surface of the part.
Step 5: Preform if uniform phosphate coating is desired, min.
Step 6: Phosphate – details are put into the phosphate bath to soak for 15-20 minutes, the phosphate layer forms on the metal surface.
Step 7: Wash water clean the surface.
Step 8: Passivation to seal the small pores on the phosphate surface to prevent yellowing.
Step 9: Drain or dry and finish the process.
Common mistakes in Phosphate process
At each stage, if it is not done with the correct technique and ratio, it will cause errors. Here are common errors and solutions:
Oil removal is not clean
Error encountered: The product is not soaked in the degreasing tank for enough time, the product is not clean in the oil and grease in the dilute degreasing tank, the phosphate layer on the surface of the product is very thin or absent.
Remedy direction:
- Control the quality of the degreasing tank in terms of the tank point index (alkalinity in the tank).
- Soak the product for enough time.
- With high-oil products, increase the amount of degreasing chemicals and have a spray operation to rinse after soaking.
- The water tank after degreasing must be continuously overflowing during the working process.
- Heating (45-65 0C) reaction as well as degreasing speed is increased and the time for degreasing process is shortened.
Rust is not clean
Error encountered: The rust removal is not clean due to the acid content in the tank is not reached or the soaking time is not enough, the technique is wrong or after the rust removal process, the product is not cleaned to remove the acid, the product after phosphate will be yellow or rusty condition.
Remedy direction:
- Soak the product for sufficient time in the descaling bath.
- Quality control of rust removal tank (acid content) is satisfactory.
- Spray to wash off the acid before going to the shaping tank.
- Quick action between the pickling tank and shaping because the product after rusting will be oxidized quickly if left out for a long time.
Shaped by the tank
Error encountered: The forming tank often has an error when the tank is highly acidic, which leads to yellowing of the product after phosphate.
Remedy direction:
Regularly check the pH of the mold to maintain it from 7-9. If it is outside this range or can be observed by the appearance of the tank from milky white to yellowish white, the tank needs to be replaced because at this time the tank is heavily acidic.
Fault in phosphate tank
The phosphate tank is the tank that produces the phosphate film. Therefore, if this tank does not meet technical standards, it will lead to a thin, unsightly phosphate film.
To overcome this situation, it is necessary to control the indicators of the phosphate tank to be within good operating standards.
>>>>>Refer to our COR H500 rust remover and phosphate solution<<<<<