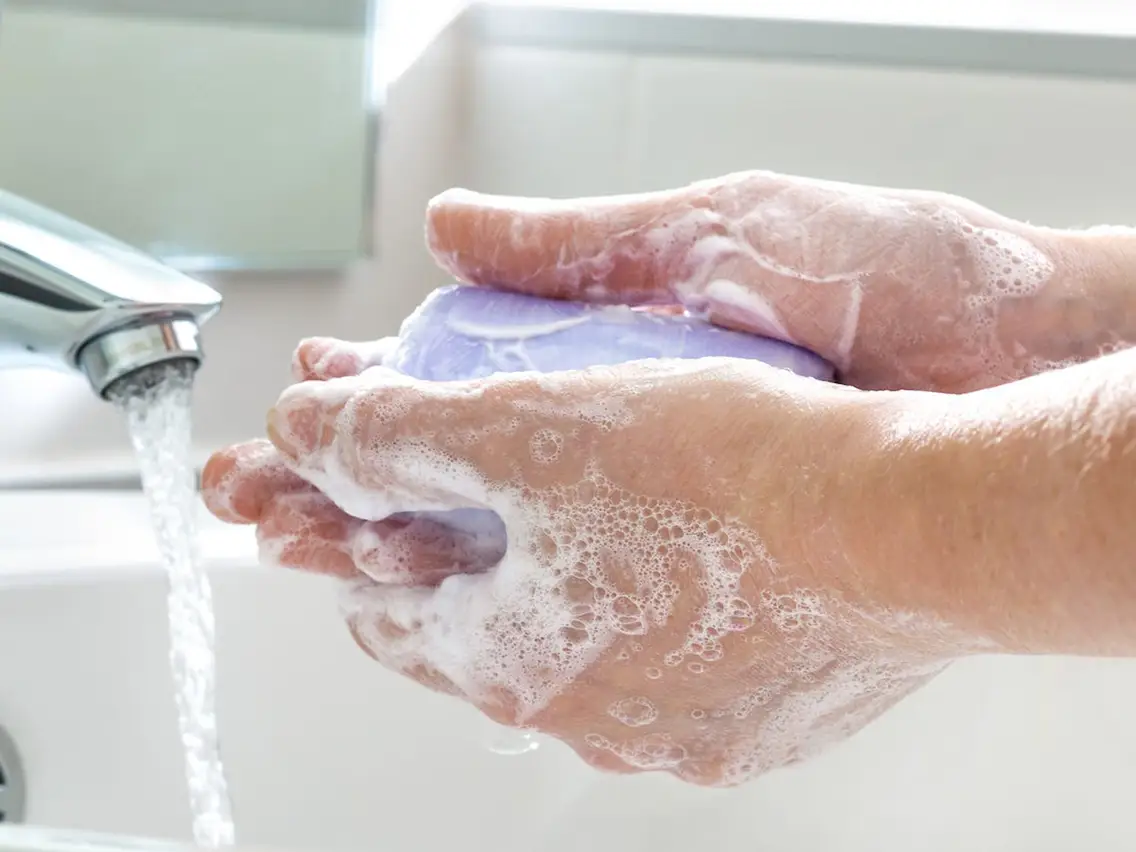
Detergent definition
Cleaning is defined as cleaning the face of a solid object with a specific agent – detergent, according to a physico-chemical process different from normal dissolution.
The cleaning process takes place according to the following steps:
- The detergent solution in water reduces the tension of the water, the water penetrates deeply into the fiber.
- The process of removing dirt.
- Anti-fouling process.
- Foaming surfactants, insoluble impurities are concentrated on the foam surface and are pushed out or dispersed into the solution in the form of a suspension, suspended.
What is detergent? The effect of detergents
Detergent definition
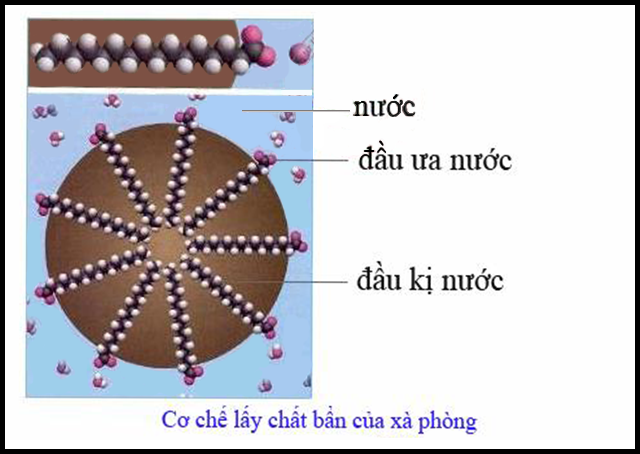
Detergent is a surfactant reduces the surface tension of water causing the fabric to be completely wetted. Each surfactant molecule has a hydrophilic end, which is attracted to water molecules, and a hydrophobic (hydrophobic) end – this end both repels water and attracts grease. These opposing forces pull the impurities out and leave them suspended in the water in dissolved, emulsion or suspension form. Stirring by hand or washing machine has helped pull the dirt out of the surface to be cleaned.
Polar stains use anionic surfactants, non-polar stains use non-ionic surfactants.
Ex: Mechanism to remove grease of soap.
Initially, fibers with greasy stains are soaked in water. Due to the high surface tension of water, the water cannot separate or dissolve the stain.
When dissolving detergent in water, this detergent solution has a lower surface tension than water. The solution can penetrate deep into the fabric and pull out the grease stains, the grease stains are removed and suspended in the form of an emulsion or a homogeneous solution.
Uses of detergents
Detergent has anti-fouling effect. Stains in bleach solutions can be hydrophilic or hydrophobic. The hydrophilic particles will disperse into the water and will not be re-adhered. In contrast, hydrophobic particles tend to stick to the fabric. In the cleaning solution, most of the fabric surface and dirt particles are negatively charged.
Anionic surfactants are attracted to dirt particles and fibers, increasing the electrostatic barrier between them and the particles, helping to stabilize the dispersion of dirt particles, preventing re-adhesion. But up to a certain concentration of stain and surfactant, the higher the anion concentration, the more re-adhesion increases due to the compression of the charged double layer covering the fiber and particle surfaces.
– The longer the molecule’s hydrophobic chain of nonionic surfactants, the greater the anti-readhesion property. The nonionic substances adsorb to the fiber surface and the dirt particles direct the hydrophilic part outward. A stereoscopic barrier is created and a layer of hydrated water prevents the particles from getting close to the fiber, preventing re-adhesion. But in fact nonionic surfactants have lower resistance to re-adhesion than anions.
– The cationic surfactant has no anti-readhesion effect, it is not suitable for washing. Cationic surfactants have a positive charge, the surface of the fabric has a negative charge, so they stick to the fabric, so they have no anti-re-adhesive effect.
Surfactants foaming causes insoluble dirt to concentrate on the foam surface and be pushed out. A surfactant or surfactant mixture with maximum foaming capacity around cmc. For a surfactant, the smaller the cmc, the greater the foaming capacity. For alkyl sulfate, the length of the carbon wire increases, the solubility cmc decreases, the foaming ability increases; When moving the hydrophilic group into the wire or using branched carbon wire, it increases cmc thereby reducing the ability to foam.
Non-ionic surfactants foam less than ions in water. To increase the foaming ability, additives are added, which are polar organic substances that can reduce the cmc of the surfactant. The foam enhancers in washing powders, dishwashing liquids, and shampoos are mono or diethanol amide creating a durable, smooth and even foam.
See more >>What is a surfactant?<<
Effect of water environment on cleaning
Hard water environment contains many Ca2+ and Mg2+ ions, which precipitate soap and reduce foam. Therefore, washing powder contains ingredients that soften water. We can use complexing agents such as ortho phosphate, pyrophosphate, diphosphate, tri phosphate (incorrect name is tripolyphosphate TPP), EDTA (ethylene Diamine Tetra-acetate), NTA (Nitrilo Tri-acetic) … But Because phosphorus-containing complexing substances will provide nutrients for plants living in the water, especially algae, making them grow quickly, so consuming a lot of O2 dissolved in water at night causes mass fish deaths. use.
Use an alkaline and buffering medium to maintain this environment. Commonly used substances such as TPP, Na2CO3, NaHCO3, silicates. In the past, people used TPP quite commonly but now Zeolites (silicates) are slowly replacing carboxylates with accelerated biodegradation polymers and new silicates are entering the market.